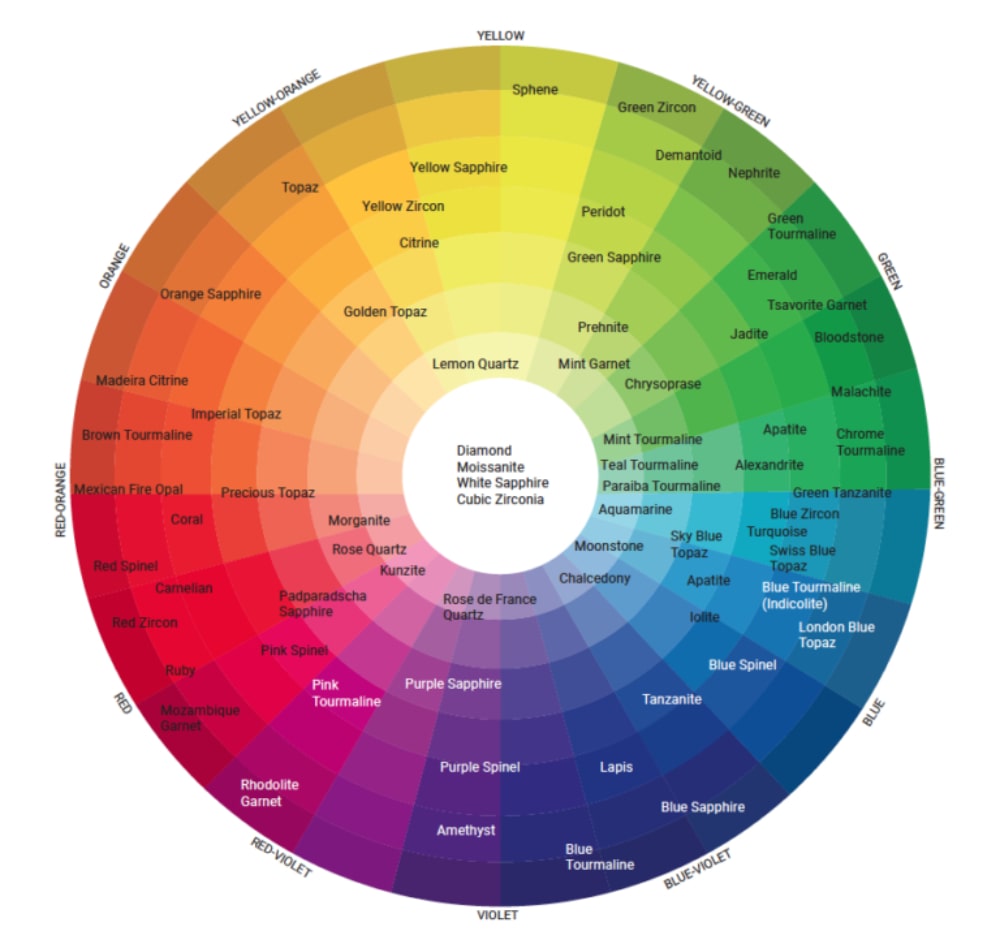
Add some color to your life! Rarity, durability, and beauty are just some of the attributes that make gemstones precious and valuable. Colored gemstones are great way to express your personality through jewelry. Your purchase may be influenced by wardrobe, favorite colors, and fashion trends. Once you have your favorite gemstone, you can tailor your jewelry to fit your sense of style.
Colored gemstones are graded similarly to diamonds with most of the focus on color. Color is graded by three different factors. Hue: the pure color on the spectrum, describes the dominant color and any additional colors visible in a gem. Tone: the lightness or darkness of a color. In the GIA color-grading system, tones range from very light to very dark. Saturation: is the purity of the hue. Gemstone are cut with the same shapes you find in diamonds such as round, rose, cushion, oval, etc., but also cabochon, checkerboard, and other specialty cuts are available.
When selecting your gemstone jewelry, select what you find beautiful. There are subtle differences in every gemstone that makes it stand out from the others. Every gemstone has an ideal hue, tone, and saturation. Our sales associates are happy to help you find the exact gemstone you desire.

Gemstone Enhancement Codes
Published by the American Gem Trade Association.
Enhancement: Any treatment process other than cutting and polishing that improves the appearance
(color/clarity/phenomena), durability, or availability of a gemstone.
N: The “N” symbol appears on the chart only for natural stones which are not currently known to be enhanced; however, the “N” symbol can also be used for other natural gemstones in the event that a gemstone has received no enhancement and the seller will provide a guarantee that there has been none.
E: The “E” symbol indicates that a gemstone has undergone its traditional enhancement process.
The processes are:
B – Bleaching: The use of heat, light and/or other agents to lighten or remove a gemstone’s color.
C- Coating: C Coating – The use of such surface enhancements as lacquering, enameling, inking, foiling, or sputtering of films to improve appearance, provide color, or add other special effects.
D – Dyeing: The introduction of coloring matter into a gemstone to give it new color, intensify present color or improve color uniformity.
F-Filling: The filling of surface-breaking cavities or fissures with colorless glass, plastic, solidified borax, or similar substances. This process may improve durability, appearance, and/or add weight.
H – Heating: The use of heat to effect desired alteration of color, clarity, and/or phenomena (if residue of foreign substances in open fractures is visible under properly illuminated 10X magnification HF should be used).
HP – Heat & Pressure: The use of heat and pressure combined to effect desired alterations of color clarity.
I – Impregnation: The impregnation of a porous gemstone with a colorless agent (usually plastic) to improve durability and appearance.
L – Lasering: The use of a laser and chemicals to reach and alter inclusions in diamonds.
O – Oiling/Resin Infusion: The filling of surface-breaking fissures with colorless oil, wax, resin, or other colorless substances, except glass or plastic, to improve the gemstones appearance.
R – Irradiation: The use of neutrons, gamma rays or beta particles (high energy electrons) to alter a gemstones color. The irradiation may be followed by a heating process.
U – Diffusion: The use of chemicals in conjunction with high temperatures to produce artificial color and/or asterism-producing inclusions.
W – Waxing/Oiling: The impregnation of a colorless wax, paraffin, and oil in porous opaque or translucent gemstones to improve appearance.